Both IELTS (International English Language Testing System) and OET (Occupational English Test) are used to test the English language of healthcare professionals in different parts of the world.
They are chosen by regulatory bodies to ensure doctors, nurses and other professions have sufficient language skills to communicate at a high level with patients and colleagues, and so ensure safe and effective care.
| Table of Contents |


There are a number of similarities between the two tests:
- Each one consists of four sub-tests, one for each skill: reading, listening, writing and speaking.
- A test takes place on one day.
- There is no pass/fail, but a graded score – different institutions need test takers to achieve different scores, such as a 7 in IELTS or a B in OET. In the UK, for example, the GMC requires doctors to score B in OET with B in each paper, or IELTS 7.5 with a minimum 7.0 in each paper. The NMC requires nurses to score B in OET with B in Reading, Listening and Speaking and a C+ in the Writing, or IELTS 7.0 with a minimum 7.0 in Reading, Listening and Speaking and 6.5 in Writing.
- In practice, the required scores in the two tests for professions such as nurses are for similar levels of language skill when measured on the Common European Framework of Reference, specifically a C1 or advanced level.
- Both tests were developed in the late 1980s and are part-owned by Cambridge Assessment English. IELTS ownership is shared with IDP and the British Council. OET ownership is shared with Boxhill Assessment.
However, that’s where the similarities end. As you will see, they are quite different tests in many ways.

-
Content
IELTS tests academic English – at least the version of IELTS used by healthcare regulatory bodies around the world. This includes the ability to write essays, follow lectures, understand academic articles and discuss a wide range of topics, from the environment to education to social trends to cultural values.
OET tests healthcare English, including the ability to communicate effectively in medical scenarios, write a referral or discharge letter, understand a patient consultation, or follow a text taken from a medical journal.
-
Versions
IELTS offers 2 versions of the test – Academic as described, and General Training, used by organisations to test the more general language considered more appropriate for immigration or vocational purposes. The Listening and Speaking sections are the same for both. The Academic Reading and Writing is more geared to Higher Education than the General Training.
OET offers 12 versions of the test for different healthcare professions; nurses, doctors, dentists, pharmacists, optometrists, podiatrists, occupational therapists, vets, speech pathologists, dieticians, physiotherapists, and radiographers. The Reading and Listening sections are the same for both. The Speaking and Writing sections are tailored to the specific scenarios in which each profession uses English.
-
Format
IELTS has the following format:
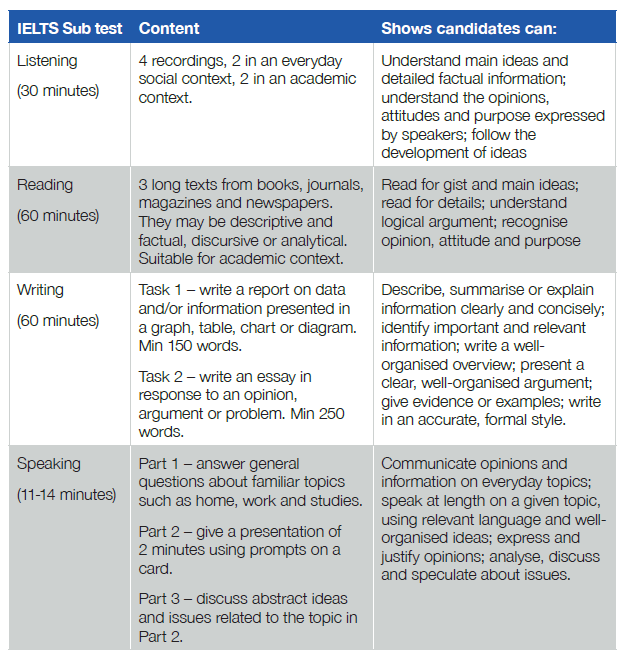
While OET has the following format:
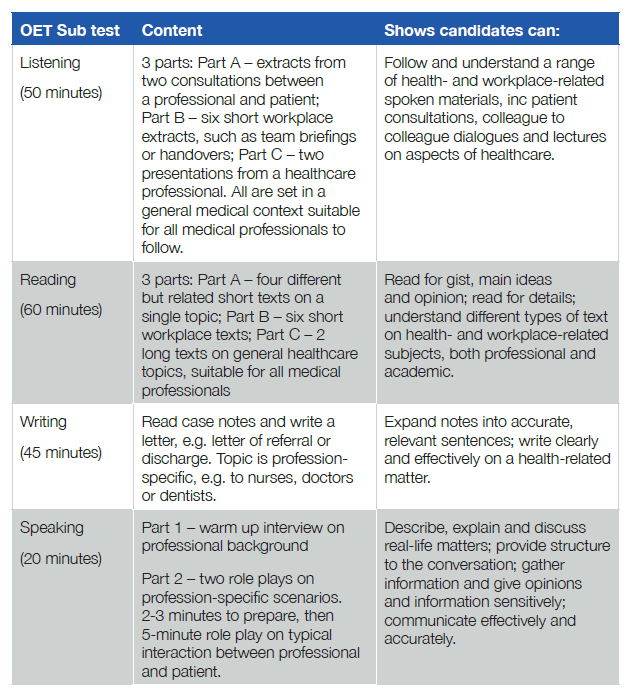
-
Preparation requirements
Preparing for IELTS involves learning huge amounts of vocabulary on a wide range of academic subjects so test takers are prepared to read academic texts quickly and effectively, understand lectures and discussions, talk about abstract questions and give opinions in detail. Test takers need to learn how to write reports on a variety of data and a range of essay types. Written texts need to be at an advanced level and so include complex structures and grammar. Learning a set of key exam techniques is also crucial.
Preparing for OET involves learning a wide range of healthcare-related and profession-specific language, so test takers are able to follow, engage with and participate in a variety of clinical scenarios, as well as understand medical texts and talks. They need to be able to write a healthcare-related letter, such as a referral letter, at an advanced level. They need to acquire a range of exam techniques so they can work quickly and effectively in the test.
As a result, preparation courses for the two tests follow very different pathways and use very different materials.
-
Scoring
IELTS is marked out of 9, with a separate score for each paper. Half marks are awarded as part of this.
OET is graded from A (best) to E, with an equivalent numerical score to show more precisely where in the grade a candidate sits.
Healthcare regulatory bodies which use both exams to test English for healthcare professions tend to specify an advanced C1 level of language, i.e. around 7 in IELTS and a B in OET. The score equivalencies between the two tests are as follows:
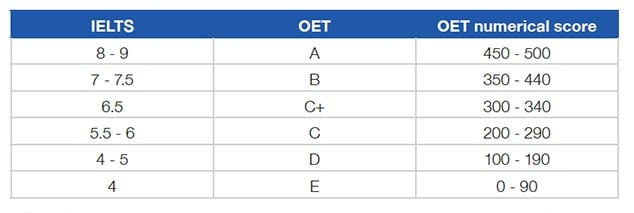
-
Recognition
IELTS is recognised by universities, regulatory bodies, immigration authorities and companies in many countries around the world. This includes universities in non-English speaking countries where a course may be delivered in English. There are over 1,100 test centres in over 140 countries.
OET is recognised by healthcare regulatory bodies and Higher Education healthcare educators, including those in the UK, Ireland, Australia, New Zealand, Singapore, Dubai, Ukraine and Namibia. There are currently 270 test centres in 49 countries.
-
Numbers of test takers
Over 3 million people took IELTS in the past year, compared to the tens of thousands taking OET. This reflects the size and reach of the global Higher Education market on the one hand and the specialist nature of the OET on the other.
-
Preparation infrastructure
IELTS has a global infrastructure developed around preparing learners to take the test, including universities, specialist training organisations, private language schools, published materials, online content, and thousands of teachers and writers.
OET has a small but global preparation infrastructure, consisting of a growing number of specialist training providers and also a small but growing materials base. OET ’s Premium Preparation Provider scheme provides a framework for training organisations to undergo a rigorous accreditation process to demonstrate their ability to prepare candidates for the specialist nature of OET. SLC was the first provider to be accredited in Europe.
Prepare for OET and IELTS
Self-study OET and IELTS Options
One-to-one OET and IELTS Coaching
Not sure what’s best for you? Then get in touch!
We are experts in both IELTS and OET preparation. We work with thousands of candidates every year and specialise in working with healthcare professionals. Clients include many NHS Trusts and private healthcare groups in the UK.




















